Stress-strain Relation
Stress-strain Relation: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Application of Elastic Behaviour of Materials, Stress-Strain Graph, Proportion Limit, Elastic Limit, Yield Strength, Breaking Point in Elasticity, Nature of Materials from Stress-Strain Graph, Permanent Set, etc.
Important Questions on Stress-strain Relation
The delay in regaining the original shape after the removal of stress is called elastic fatigue.
The material which practically does not show elastic after effect is
The delay in returning to its original shape by a substance after removing the applied force is called _____.
What is elastic after effect? Mention its application.
What is the reason of low toughness of grey cast iron
Which factor decreases toughness of material
The property of a material which enables it to absorb energy and deform plastically without fracture is
The ability of a material to undergo plastic deformation without rupture, when a compressive force is applied, is known as
The ability of a material to undergo plastic deformation without fracture when subjected to uniaxial tensile force is
Which of the following is not a brittle material.
When a wire is loaded beyond the elastic limit and then reloaded. The work done disappears completely as heat.
The elastic behaviour of a body can be turned into plastic behaviour under the larger deforming force.
What do you understand by the plastic deformation of a body?
A steel wire of uniform cross-section of is heated to and stretched by tying its two ends rigidly. What is the change in the tension of the wire (in SI units) when the temperature falls from to ? Coefficient of linear expansion of steel is ( and Young's modulus is )
A steel wire of length and cross section is hung from a rigid support with a steel weight of volume hanging from the other end. Find the decrease in the length of wire, when steel weight is completely immersed in water.
and (Density of water (Take )
A sphere of mass is attached at one end of a steel wire having length and radius . It is whirled in a vertical circle with an angular velocity of . What is the elongation of wire, when sphere is at lowest point in its path? (Take)
A particular force () applied on a wire increases its length by To increase the wire's length by the applied force must be
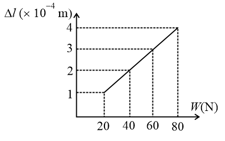
The adjacent graph shows the extension () of a wire of length suspended from the top of a roof at one end and with a load connected to the other end. If the cross-sectional area of the wire is , calculate the Young's modulus of the material of the wire.
A wire has length and area . The work required to increase its length by is
